Introduction to Air Bags: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Their Function and Safety Measures
In today’s fast-paced world, safety is of paramount importance, especially when it comes to automobiles. With the advancements in technology, air bags have become an essential component in automotive safety systems, providing protection to occupants in the event of a crash. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of air bags, exploring their function, the crucial role of sensors in their activation, and the speed at which they deploy. Furthermore, we will uncover the intricate process of inflating and deflating these life-saving devices and explore post-accident safety measures. Join us on this journey of unraveling the mysteries behind air bags and discover how they effectively safeguard lives on the road.
Introduction to Air Bags
An Introduction to Air Bags
When it comes to vehicle safety, air bags play a crucial role in protecting drivers and passengers during accidents. Air bags are inflatable cushions that are strategically placed throughout a vehicle. They are designed to deploy rapidly in the event of a collision and provide a cushioning effect that reduces the impact force on the occupants. Understanding how air bags function can help us appreciate their importance in ensuring our safety on the road.
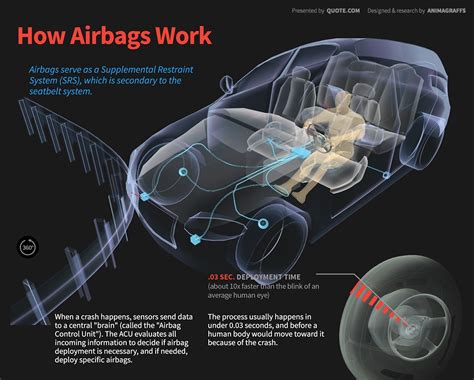
First and foremost, it is essential to note that air bags are not standalone safety features. They work alongside seat belts to provide maximum protection in the event of a crash. Together, they form a comprehensive safety system that can significantly reduce the risk of serious injuries or fatalities.
When a vehicle collides with an object or another vehicle, it experiences a sudden change in momentum. This change in momentum causes the vehicle’s sensors to detect a significant deceleration and triggers the air bag deployment system. The air bag sensors, which are strategically placed throughout the vehicle, play a crucial role in sensing the severity of the impact and determining whether air bag deployment is necessary.
- The Function of Air Bag Sensors
- Activation of the Air Bag System
- Inflating the Air Bag
- Air Bag Deployment Speeds
| Type of Air Bag | Average Deployment Speed |
|---|---|
| Driver Air Bag | 200 mph |
| Passenger Air Bag | 200 mph |
| Side Air Bag | 90 mph |
Once the air bag system is activated, the air bag inflates rapidly, providing a cushioning effect to reduce the impact forces on the occupants. The inflation process occurs within milliseconds, ensuring that occupants are protected even before they come into contact with the vehicle’s interior or other objects. This rapid deployment and inflation greatly contribute to the effectiveness of air bags in preventing severe injuries.
Protecting occupants in a crash is the primary objective of air bags. By absorbing the impact forces and preventing direct contact between the occupants and the vehicle’s interior, air bags greatly reduce the risk of head, chest, and other upper body injuries. However, it is important to note that air bags are most effective when used in conjunction with seat belts. Therefore, it is vital to always buckle up and ensure that all vehicle occupants are properly restrained.
After a collision, air bags deflate rapidly to allow occupants to exit the vehicle safely. The deflation process occurs almost instantaneously, minimizing any potential obstruction to occupant egress. Furthermore, post-accident air bag safety measures are in place to prevent accidental deployment or re-inflation of the air bags, ensuring the safety of rescue personnel and occupants.
Conclusion
Air bags have revolutionized vehicle safety by significantly reducing the risk of serious injuries and fatalities during accidents. Understanding the functioning of air bags and their importance in protecting occupants highlights the significance of utilizing this critical safety feature in all vehicles. Remember, air bags work in tandem with seat belts, so always ensure that you and your passengers are buckled up for every journey.
The Function of Air Bags
When it comes to car safety, air bags play a vital role in protecting passengers during an accident. The function of air bags is to act as a supplement to seat belts, providing an additional layer of protection in the event of a crash. Air bags work by rapidly inflating and deflating to cushion the impact and reduce the risk of injury.
There are several key components involved in the functioning of air bags. One of the most important components is the air bag sensor. These sensors are strategically placed throughout the vehicle and are responsible for detecting sudden deceleration or impact. When the sensors detect a significant collision, they send a signal to the air bag control module.
The air bag control module is like the brain of the air bag system. It receives signals from the sensors and determines if deploying the air bags is necessary. If the module determines that deployment is required, it sends a signal to the inflator to initiate the process. The inflator contains a chemical mixture that rapidly produces gas to fill the air bag.
- Sensors: detect collision or impact
- Air bag control module: receives signals from the sensors and determines if deployment is necessary
- Inflator: contains a chemical mixture that rapidly produces gas to fill the air bag
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Sensors | Detect collision or impact |
| Air bag control module | Receive signals from sensors and determine if deployment is necessary |
| Inflator | Contain a chemical mixture that rapidly produces gas to fill the air bag |
Understanding Air Bag Sensors
When it comes to car safety, air bags play a crucial role in protecting occupants during a collision. But have you ever wondered how air bags actually work? One of the key components in any air bag system is the sensors. These sensors are designed to detect sudden changes in vehicle motion and trigger the deployment of air bags when necessary. In this blog post, we will delve deeper into the world of air bag sensors and explore their function in ensuring passenger safety.
First and foremost, it’s important to understand that air bag sensors are strategically placed throughout the vehicle. These sensors are typically located in the front of the vehicle, near the front bumper or behind the grille. They are specifically designed to measure changes in momentum and deceleration, which are potential indicators of a collision. When a rapid deceleration is detected, the sensors send a signal to the air bag control module, initiating the deployment sequence.
So, how do these sensors actually work? There are different types of air bag sensors used in modern vehicles, but the most common ones are accelerometer-based sensors. These sensors utilize microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) to measure changes in acceleration. When a collision occurs, the vehicle experiences a rapid deceleration, which causes the mass inside the sensor to move. This movement is then converted into an electrical signal, indicating that the air bags should be deployed.
In addition to accelerometer-based sensors, some vehicles also incorporate advanced sensors such as gyroscopes and pressure sensors. Gyroscopes can detect rotational movements of the vehicle, providing additional data to enhance the accuracy of air bag deployment. Pressure sensors, on the other hand, can measure changes in the vehicle’s cabin pressure, which can help determine the severity of a collision and adjust air bag deployment accordingly.
Overall, air bag sensors are integral to the proper functioning of a vehicle’s air bag system. They serve as the first line of defense by detecting potential collisions and triggering the necessary safety measures. By understanding how these sensors work, we can appreciate the complex technology behind air bag systems and our own safety on the road.
- Understanding the role of air bag sensors in vehicle safety
- The different types of air bag sensors and their functions
- The technology behind accelerometer-based sensors and their operation
- Advanced sensors like gyroscopes and pressure sensors
- The importance of air bag sensors in ensuring timely and accurate deployment
| Pros of Air Bag Sensors | Cons of Air Bag Sensors |
|---|---|
| Enhance occupant safety by detecting collisions | Possibility of false deployment in certain scenarios |
| Can adjust air bag deployment based on collision severity | Require regular maintenance and calibration |
| Provide valuable data for post-accident analysis | May not always activate in highly localized collisions |
Activation of the Air Bag System
When it comes to car safety, one of the most crucial components is the activation of the air bag system. In the event of a collision, air bags are designed to deploy rapidly and provide a cushioning effect to reduce the impact on occupants. But how exactly does the air bag system know when to activate? Let’s take a closer look at the function of air bag sensors and the process of air bag deployment.
Air bag sensors play a vital role in determining when the air bag system should be activated. These sensors are strategically placed throughout the vehicle and are designed to detect sudden deceleration or impact. They constantly monitor various parameters such as vehicle speed, acceleration, and direction of impact. In the event of a crash, the sensors send a signal to the air bag control module, which triggers the deployment of the air bags. This is a critical step in ensuring that the air bags are only activated when necessary, preventing unnecessary deployment in non-impact situations.
Once the air bag system receives the signal from the sensors, the inflating process begins. The air bag module rapidly releases a combination of chemicals, typically sodium azide or potassium nitrate, which undergo a chemical reaction to produce a large volume of gas. This gas inflates the air bag within milliseconds, providing a protective cushioning barrier between the occupants and the interior of the vehicle. The whole process is designed to happen so quickly that occupants may not even be aware of the inflation until after it has occurred.
Inflating the Air Bag
When it comes to car safety, air bags are one of the most important features that provide protection to the occupants during a crash. One crucial aspect of air bags is their ability to inflate rapidly in order to cushion the impact and reduce the risk of severe injuries. In this blog post, we will delve into the process of inflating the air bag and understand the mechanisms behind it.
Firstly, it is important to note that air bags are not continuously inflated while the vehicle is in motion. Instead, they remain deflated until a crash occurs. The moment a collision is detected, the air bag sensors send a signal to the air bag control module, informing it of the impact. This triggers the inflation process.
The inflation of an air bag occurs in a matter of milliseconds and involves the deployment of stored gas. The air bag module contains a mixture of sodium azide and potassium nitrate, which are highly reactive substances. When the crash sensors detect a rapid deceleration, an electrical current is sent to ignite a small explosive device, which in turn generates nitrogen gas to inflate the air bag rapidly.
Air Bag Deployment Speeds
When it comes to air bag deployment speeds, there are several crucial factors to consider. Air bags are designed to deploy rapidly in order to protect occupants during a collision. The deployment speed plays a vital role in ensuring the effectiveness of air bags in minimizing injuries. Let’s delve deeper into this aspect of air bag technology.
First and foremost, it’s important to understand that air bag deployment speeds can vary depending on the specific situation. The speed at which an air bag deploys is determined by various sensors and electronic control units within the vehicle. These sensors detect the severity of the impact and send signals to the air bag system, triggering the deployment process.
There are different sensors utilized to measure impact forces and determine the appropriate deployment speed. These sensors include accelerometers, crash sensors, and pressure sensors, among others. They work together to collect data and calculate the required deployment speed for maximum protection.
Protecting Occupant in a Crash
When it comes to automobile safety, one of the most important features that comes to mind is the air bag. Air bags are designed to provide an additional layer of protection to the vehicle occupants in the event of a crash. These safety devices have saved countless lives over the years and continue to play a crucial role in reducing the severity of injuries during accidents.
The function of air bags is to serve as a cushioning barrier between the occupants and the hard surfaces of the vehicle’s interior. In a crash, the air bag rapidly inflates with gas, creating a soft and cushioned landing spot for the occupants’ bodies. This helps to distribute the force of impact across a larger surface area, reducing the risk of serious injuries such as head trauma or broken bones.
Understanding air bag sensors is vital to comprehend how these safety devices are activated. Air bag sensors, typically located throughout the vehicle, are designed to detect sudden deceleration or impact forces. These sensors monitor the vehicle’s movements and, when a crash is detected, they send a signal to the air bag system to activate. This quick response is crucial in providing protection to the occupants in the shortest possible time.
- The air bag system consists of several components, including:
- Sensors
- Air bag module
- Inflator
- Control unit
During a crash, the activation of the air bag system is triggered by the sensors, which send a signal to the control unit. The control unit then initiates a rapid sequence of events. First, the inflator generates a gas that rapidly fills the air bag. The air bag then deploys from its storage location, usually located in the steering wheel, dashboard, or side panels of the vehicle. Within milliseconds, the air bag is fully inflated and ready to protect the occupants from the impact of the crash.
The speed at which the air bag deploys is carefully designed to provide optimal protection. The deployment speed is influenced by various factors, such as the severity of the crash, the occupant’s position, and the type of collision. Modern air bag systems are equipped with advanced technologies that allow for adaptive deployment, meaning the system adjusts the deployment force and speed according to the crash situation, ensuring maximum safety for the occupants.
Once deployed, the air bag plays a crucial role in protecting the occupants in a crash. It acts as a buffer between the occupant’s body and the hard surfaces of the vehicle’s interior, mitigating the impact force and reducing the risk of serious injuries. It is important to note that air bags are designed to work in conjunction with seat belts, as they complement each other’s functionality. The combination of seat belts and air bags provides the highest level of protection for vehicle occupants.
After a crash, the air bags deflate to prevent obstructing the exit paths or hindering the rescue operations. The air bag deflation process is designed to occur gradually, ensuring that the occupants are not trapped inside the vehicle. Once the crash forces subside, the air bag modules deflate through small vents, allowing the occupants to exit the vehicle safely.
In conclusion, air bags are an essential safety feature that plays a vital role in protecting occupants in a crash. By cushioning the impact, reducing the risk of severe injuries, and working in tandem with seat belts, air bags contribute significantly to saving lives on the road. Understanding how air bags function and ensuring their proper maintenance and functionality are crucial for maximizing their effectiveness and keeping vehicle occupants safe.
Air Bag Deflation Process
An air bag deflation process is an important part of the overall functioning of an air bag system. After an air bag has deployed and served its purpose during a crash, it needs to be deflated to ensure the safety of the occupants. The deflation process of an air bag involves a series of steps that occur once it has been activated.
The first step in the air bag deflation process is the release of gas. When an air bag is deployed, it is filled with nitrogen gas or a combination of nitrogen gas and a small amount of argon gas. This gas is released from the air bag through small vent holes located on its surface. The release of gas allows the air bag to gradually deflate.
Next, the deflation process involves the folding and compression of the air bag. As the gas is released, the air bag starts to deflate and fold in on itself. This folding and compression helps to reduce the size of the air bag and make it easier to be safely contained within the vehicle. The folding and compression process also allows for a smoother deflation of the air bag.
Post-Accident Air Bag Safety Measures
After a vehicular accident, the safety measures related to air bags go beyond their initial deployment. It is essential to understand the importance of post-accident air bag safety procedures to ensure the well-being of everyone involved and to prevent further harm. Let’s explore some key measures that need to be taken after an air bag has been deployed.
1. Inspect and Assess
Once the accident has occurred and the air bags have deployed, the first step is to inspect the vehicle and assess any damage caused. Carefully examine the condition of the air bags and the surrounding areas for any signs of malfunction or problems. Look for any tears or punctures in the air bag material, as these could compromise their ability to provide protection in the future.
2. Seek Professional Assistance
If you are unsure about the condition of the air bags or if you notice any issues during the inspection, it is crucial to seek professional assistance. Take your vehicle to a certified mechanic or contact the manufacturer for further evaluation. They have the expertise and knowledge to determine if the air bags need to be replaced or if any repairs are necessary.
3. Reset the Air Bag System
After the inspection and potential repairs, it is essential to reset the air bag system if it has been triggered during the accident. This process ensures that the air bags are functioning correctly and are ready to deploy if needed in any future accidents. Refer to the vehicle’s manual or consult a professional to correctly reset the air bag system.
4. Use Appropriate Restraints
Even if the air bags have deployed in a crash, it is crucial to remember that they are not the sole means of protection. Always use seat belts and child restraints properly, as they work in conjunction with air bags to provide maximum safety. Ensure that everyone in the vehicle is securely buckled up, regardless of whether the air bags have been deployed or not.
5. Regularly Maintain and Replace
Finally, post-accident air bag safety measures also include regular maintenance and potential replacement of the air bags. Over time, air bags can deteriorate or become less effective due to environmental factors, such as heat or humidity. It is necessary to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and replace the air bags at designated intervals to ensure their optimal performance.
By adhering to these post-accident air bag safety measures, you can help ensure the ongoing protection of yourself and your passengers. Remember, air bags are designed to work alongside other safety features, so it is crucial to prioritize all aspects of vehicular safety to minimize the risk of injuries in any road accident.